Products for Creating Motion and Flow
Quick Navigation
Automation | Automotive / Fleet | Compressed Air & Gas Distribution & Treatment | Control Products - Industrial | Control Products - Mobile Equipment | Couplings & Fittings | Cylinders & Actuators | Electrical System Controls & Accessories | Electromechanical Products | Filters & Filtration | Gaskets, Seals & O-Rings | Hoses | Hydraulics | Instrumentation & Process | Kits | Lubricants, Sealants & Cleaners | Pneumatic Products | Pressure Washer Accessories | Pumps | Quick Disconnects | Tools & Equipment | Tube Assemblies & Tubing | Valves
We are working hard to bring you the best quality products in the industry. That is why we only partner with the most reliable brands you will find anywhere.
We are here not only to help you source the best parts for your hydraulic, pneumatic, electromechanical, and other industrial applications, but also to support your operations with services that make your job easy and your business more efficient.
We have been solving hydraulic and pneumatic challenges for over 60 years! Many of our Technology Managers, engineers, and leaders previously worked for leading motion and flow product manufacturers like Parker Hannifin. We know our products, and we understand your industry. Take advantage of our expertise – we'll be thrilled to help you
We Are Parker Chomerics DistributorChomerics Division is a global leader in the development and application of electrically conductive and thermal interface materials for electronics, life science, aerospace, automotive, and other markets. |
Product Questions

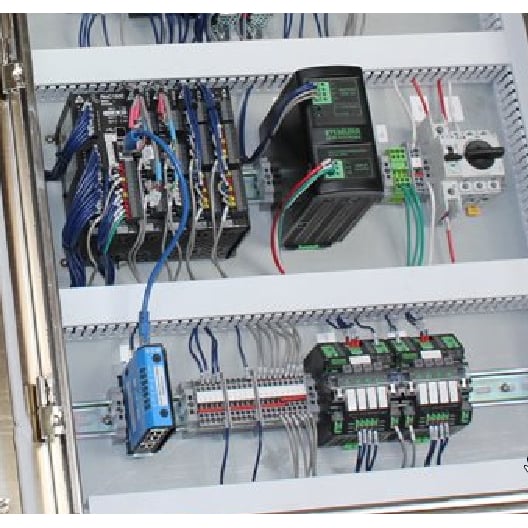
Products

Harness Solutions

& Video

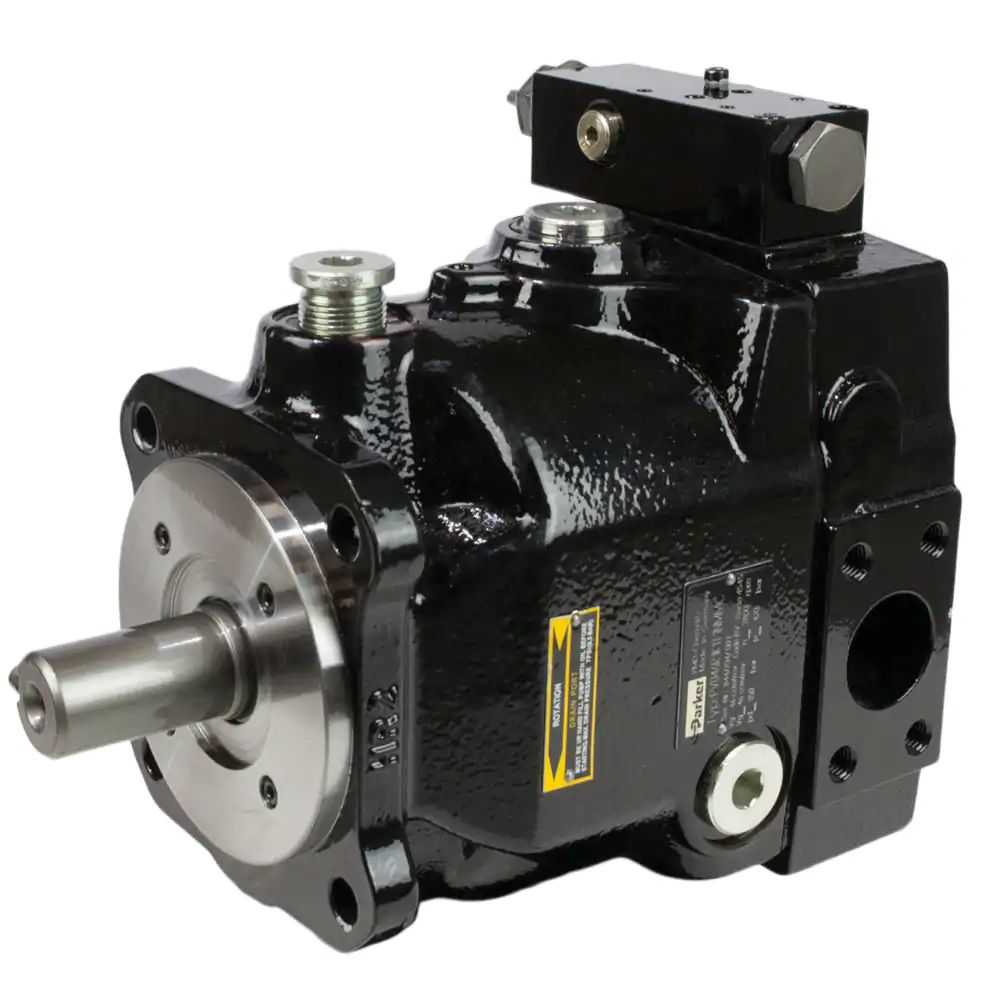
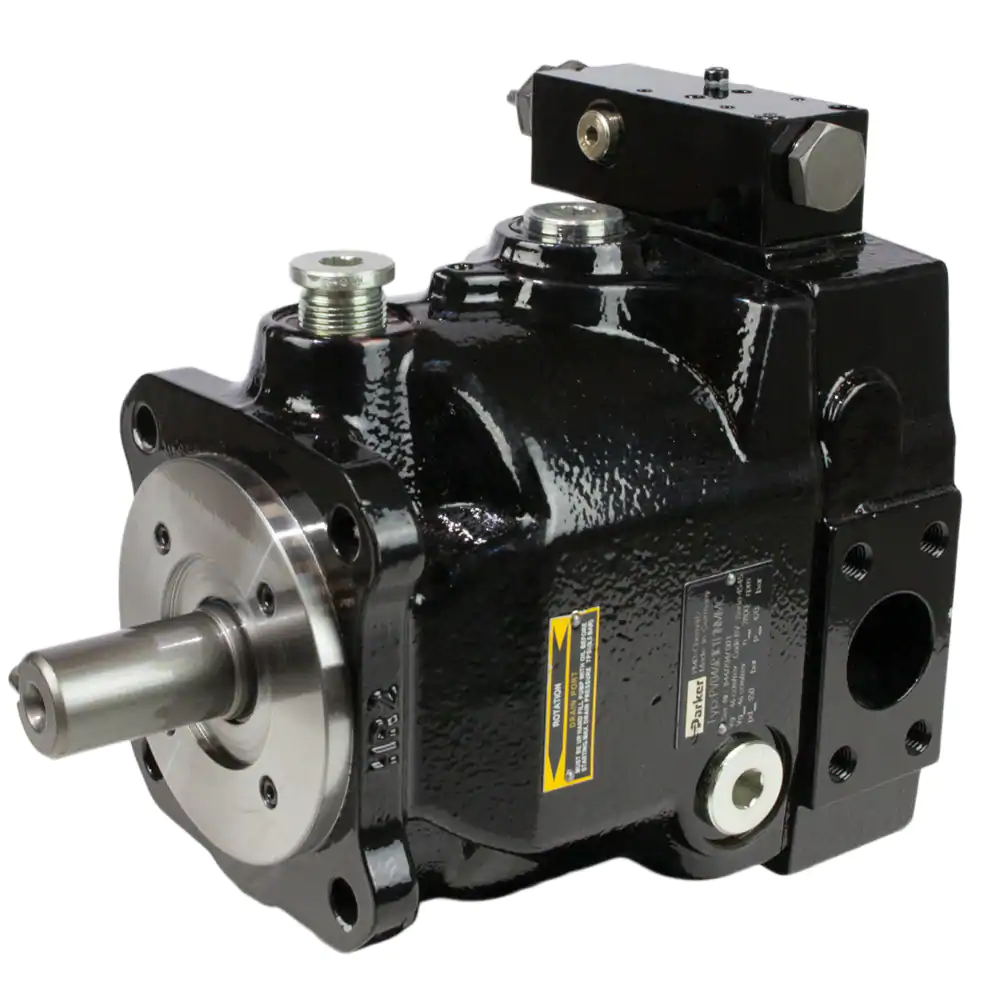
Hydraulics

HMI Centers

& Cylinders

I/O Modules

Telematics
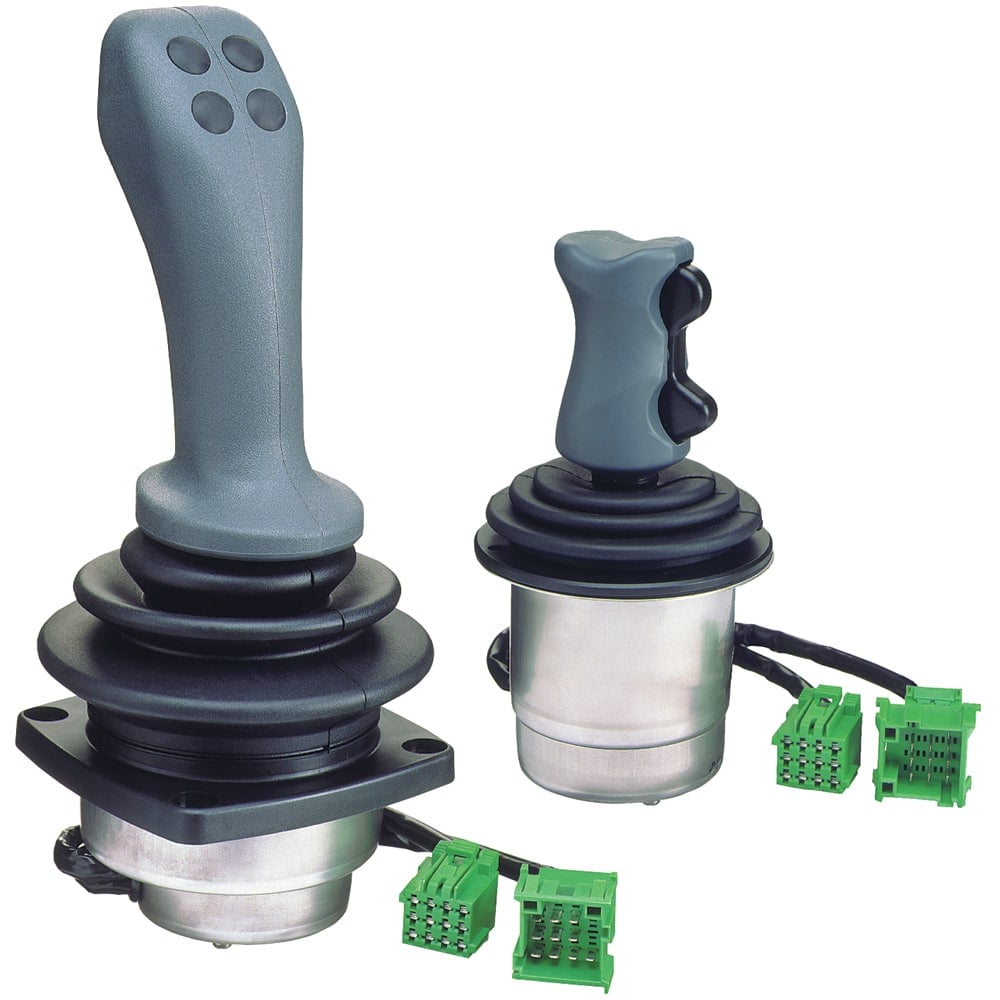

& Levers
Beacons
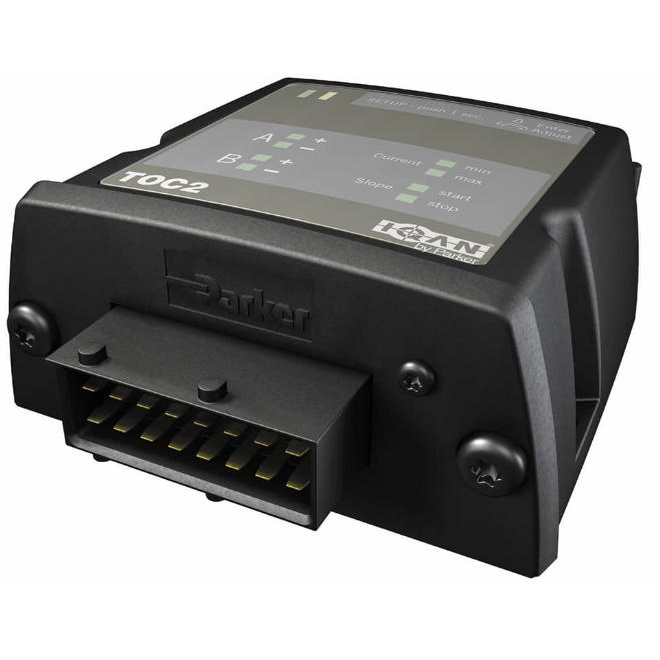

Controllers
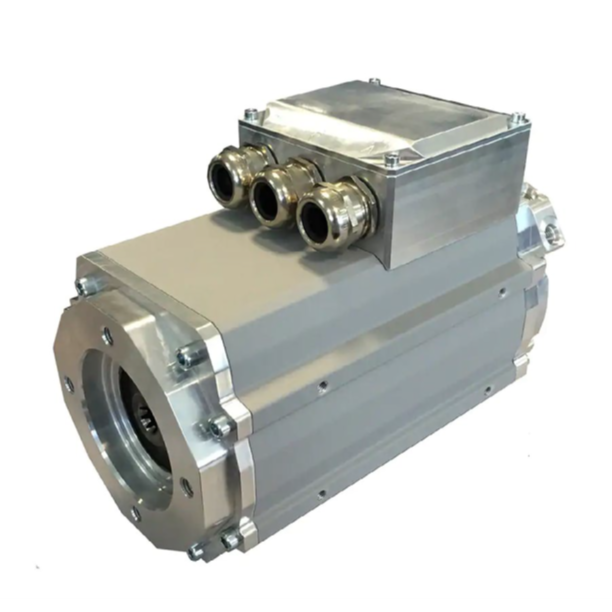

& Drives

Interfaces

Management

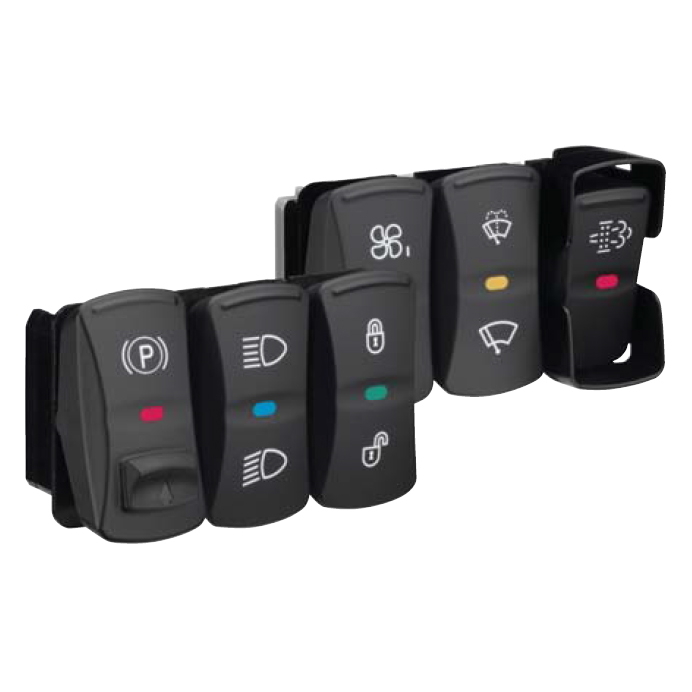
& Switches

Radio Controls

Hoses

Assemblies

Hydraulic
Hoses

Hoses

Hoses

/PTFE Hoses

1-Wire
Hoses

2-Wire
Hoses

4-Wire
Hoses

6-Wire
Hoses

Fiber-Reinforced
Hoses

Metal Hoses

Purpose Hoses

Fuel Hoses

Hoses

Hoses

Hoses

Hoses

Hoses

Hoses

Hoses

Dispenser Hoses

Hoses

Hoses

Hoses
Accessories